May 2022


Market Summary
As 2021 came to a close, the retail sector was recovering largely in part due to its strong economic foundations. However, this was not the case for all retail types as some saw no change or even negative sales partly due to the inability to adapt to new supply chains. In the first year after the pandemic, foot traffic at brick and mortars was up 25% which is great considering nearly $900 billion with online merchants was recorded. This shows a hybrid demand with E and M-commerce options accompanied by physical stores. Nevertheless, many non-essential, supply stores did close down as there was a shift in consumer spending.
In 2021, with the relaxing of the most stringent of the Covid rules, the US regained the lead in the global retail market followed closely by China. The lead was in part due to the strong purchasing power of domestic consumers. For established businesses and new business with innovative strategies and consumer-oriented service models, this is great. New entrants without an edge will struggle. The forecast for 2022 is great considering the trends seen in 2021, but with geopolitical shifts such as the Russia-Ukraine war and the potential consequences from that, questions remain.
Key Takeaways
Key highlights that shaped the 2021 retail market are as follows:
- Foot traffic grew with shopping centers seeing an increase up to 25% from 2020 levels.
- $870B was recorded by online merchants growing the E-commerce segment by 14%.
- Demand for certain luxuries decreased while consumers received free cash in the form of stimulus checks from the government which increased their shopping power.
- The retail availability rate fell.
- Net absorption sustained positive demand.
- New supply fell.
- Average asking rent increased by 1.6%.
- Over 40,000 leases were signed during the first two quarters of 2021.
- There was a net growth in the number of stores while the previous year saw a net loss of over 6,000 stores.
- Malls saw a positive amount of traffic.
- Black Friday shopping was above 2020 levels, but they were not back to pre-pandemic levels.
- Out of stock indicators were up over 250%.
- Clothes and shoes were highly elevated.
Indicators of success with potential setbacks are discussed in the next two sections. In this report, it is shown how consumer spending behavior changed during and after the pandemic with an increase in durables, and hoarding, along with a fall in services. There was initially an increase in need-based spending, but with the rise of influencer marketing, luxury sales saw a rise. The demand for retail space and investment in that space are both on the rise. The Mall REITs case study shows how what was feared to be abandoned actually performed better than before.
Key Indicators
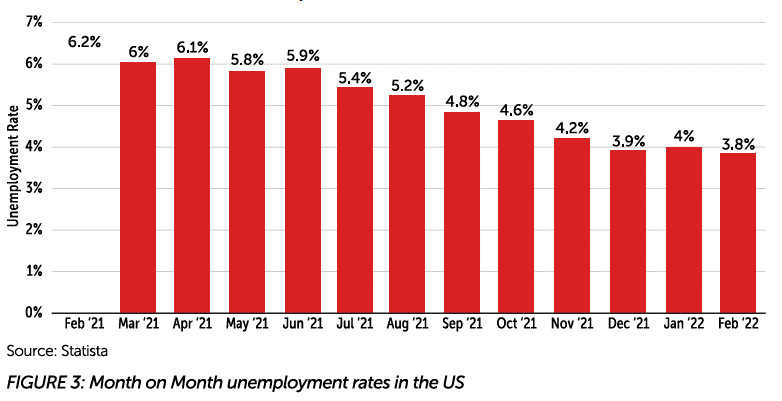
The key indicators for a promising economic recovery and retail market growth are due to the following:
- The unemployment rate dropped to its lowest rate since 2010.
- This is shocking as 2020 saw the highest unemployment rate since 2008 due to the sudden layoffs and business closures. This can be seen in the figure above.
- Labor force participation rate was improved due to the pandemic shutdowns being lifted.
- As many as 430,000 new jobs were added to the economy by March of 2022.
- Corporate profits have risen nearly a quarter from pre-pandemic levels.
- Strong profits have led to increased business investment and the willingness to invest in new age technologies and strategies along with the traditional ones.
- Labor productivity has accelerated and is nearly double what was predicted.
The negative indicators going into the new year are as follows:
- Russia invaded Ukraine causing a geopolitical shift. Consequently, inflation levels are expected to increase.
- This is because Russia produces about 12% of global crude oil supplies. US sanctions would remove this oil from the market increasing the cost of other products.
- The EU relies on Russian natural gas, so their supply chain will be strained.
Predictions
Quarter 1 of 2022 relied heavily on the unfolding of the Russia-Ukraine situation, continued inflation, and fluctuating Covid-19 levels. Before the war, projected growth rates in the US were higher, but due to the implementation of sanctions, there’s been a sudden dent. This dent is not enough to undo the overall recovery which is being positively impacted by low employment rates, high labor force participation, Consumer Price Index, Gross Domestic Product growth rate, inflation rates, and more.
The low unemployment rate is one of the largest factors at play with four significant organizations offering similar opinions. The Federal Reserve predicts the decrease will remain even into 2023 reaching 3.5%. The International Monetary Fund projects a decrease to 3.7%. The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development expects a decrease but only to 4.3%. Lastly, the European Commission predicts the lowest decline to 3.4%. GDP Growth is estimated to be slower in 2022 with inflation. Rate hikes are to be expected until inflation is deemed under control.
In March of 2022, the consumer price inflation increased by 8.5%, the highest level in the past 4 decades. This could hurt US economic growth depending on consumer spending. During the pandemic, households were able to save a good amount of money creating optimism towards purchase power, but the power is being offset by the inflation. Consumers will either remain cautious or have a spending boom.


